Compiler driver
-
Most compilation systems provide a
compiler driverthat invokes the language preprocessor, compiler, assembler and linker, as needed on behalf of the user. -
Consider the example C program below:
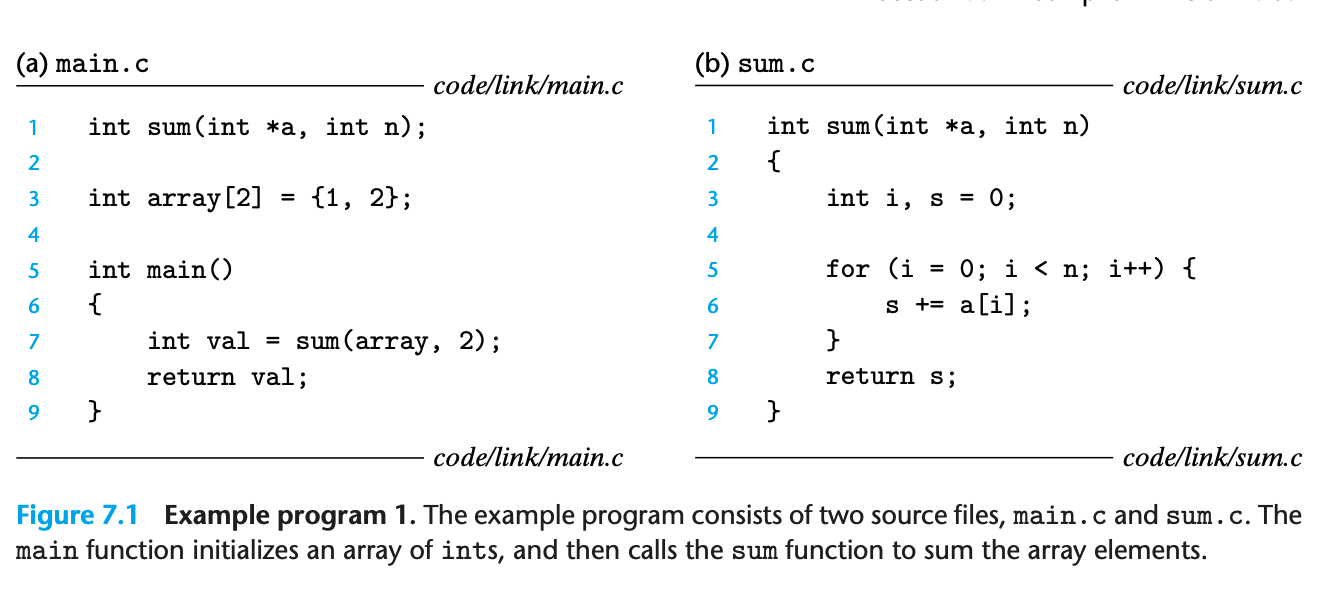
-
To build this example, we might invoke the
gccdriver by typing the following command to the shell:Terminal window gcc -Og -o prog main.c sum.c# O = big o, not zero -
Figure 7.2 summarizes the activities of the driver as it translates the example from an ASCII source file into an executable object file.
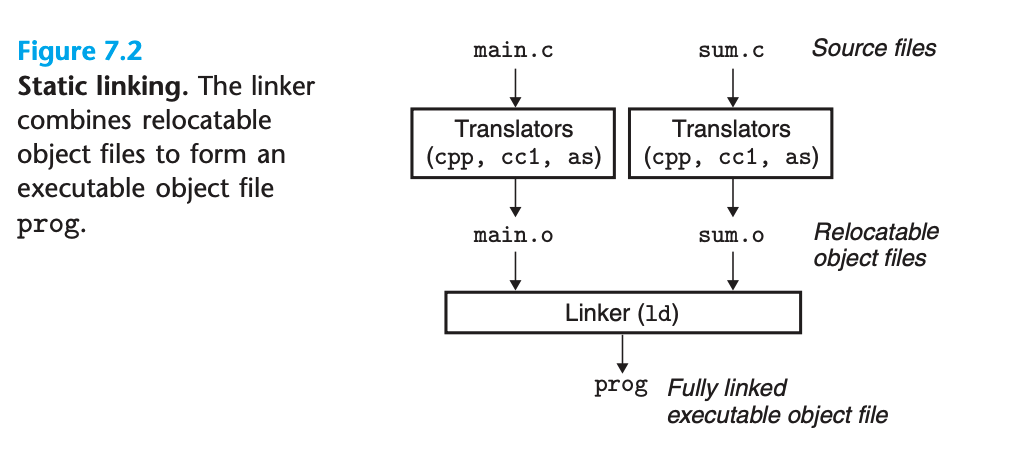
- The driver first runs the C preprocessor (cpp), which translates the C source file
main.cinto an ASCII intermediate filemain.iTerminal window cpp main.c main.i - Next, the driver runs the C compiler (gcc), which translates
main.iinto an ASCII assembly-language filemain.s:Terminal window gcc -S main.i -Og -o main.s - Then, the driver runs the assembler (
as), which translatesmain.sinto a binaryrelocatable object filemain.o:Terminal window as -o main.o main.s - The driver goes through the same process to generate
sum.o. Finally it runs the linker programld, which combiesmain.oandsum.o, along with the necessary system object files, to create the binaryexecutable object fileprog:Terminal window ld -o prog main.o main.s - To run the executable
prog, types its name on the shell:Terminal window ./prog - The shell invokes a function in the OS called the
loader, which copies the code and data in the executable fileproginto memory, then transfers control to the beginning of the program.
- The driver first runs the C preprocessor (cpp), which translates the C source file
Object files
-
Object files come in 3 forms:
- Relocatable object file: Contains binary code and data in a form that can be combined with other relocatable object files at compile time to create an executable object file.
- Executable object file: contains binary code and data in a form that can be copied directly into memory and executed.
- Shared object file: a special type of relocatable object file that can be loaded into memory and linked dynamically, at either load time or run time.
-
Formats:
- Windows: Portable Executable (PE) format.
- Linux/Unix: Executable and Linkable format (ELF).