Processes Credentials
- Note that owner of the process != owner of the program
User ID (UID) and Group ID (GID)
- Every user has a unique login name and an associated numeric user identifier (
UID). - Users can belong to one or more groups. Each group also has a unique
name and a group identifier (
GID).
mc@gmktec-server:~$ grep $LOGNAME /etc/passwdmc:x:1000:1000:chuhuynh:/home/mc:/bin/bash
#mc = Login name#x = Encrypted password#1000 = UID#1000 = GID#chuhuynh = Comment#/home/mc = Home directory#/bin/bash = Login shellReal User ID (RUID) and Real Group ID (RGID)
- The real user ID and group ID identify the user and group to which the process belongs (the UserID of the user that started the process)
- In our shell, every process that we’ll now run will inherit the privileges of my user account and will run with the same UID and GID.
mc@gmktec-server:~$ sleep 100 & ps aux | grep 'sleep'[1] 22642mc 22642 0.0 0.0 5684 1920 pts/0 S 14:02 0:00 sleep 100mc 22644 0.0 0.0 6544 2304 pts/0 S+ 14:02 0:00 grep --color=auto sleepmc@gmktec-server:~$ stat -c "%u %g" /proc/22642/1000 1000- In this case, those are the
RUIDandGUIDof the process (not the program)
Effective User ID (EUID) and Effective Group ID (EGID)
-
EUIDdetermines the permissions that the process has while executing a particular task. -
It can change during the execution of a process, allowing the process to temporarily gain additional permissions beyond those granted by the real
UID. -
By default,
EUIDandEGIDare the same asRUIDandRGID. But asetuidprogram may run withEUIDthat differs from itsRUID, enabling it to perform tasks that require higher privileges for specific operations. -
Let take
passwdprogram as an example:
mc@gmktec-server:~$ ls -l /usr/bin/passwd-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 64152 Apr 9 07:01 /usr/bin/passwd
# This program belongs to root user# How can mc user run passwd program if mc doesn't have root privilege ?-
Notice the ‘s’ letter instead of ‘x’ in the owner part of the file permission. This is a special permission bit for specific binary executable files which is known as
setuid. -
When a
setuidbinary likepasswdexecutes, the process changes itsEUID(from the defaultRUID) to the owner of this special binary executable (rootin this case).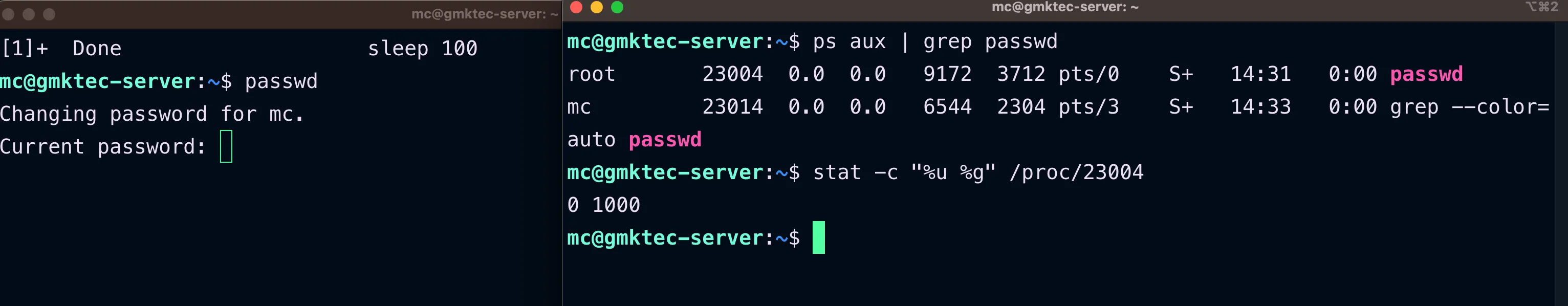
- The process
passwdis run as root user
- The process